EVENT: Roocon 2025

I attended RooCon 2025 and learned so many things about APT, and APT groups. This blog contains information I gathered from the event and my research afterwards.
TALK1: Breaking the Ice on IIS post-exploitation frameworks
Speaker: Adrian Justice
This talk covers the discovery of IIS post exploitation framework by OverWatch (threat hunting service by CrowdStrike) in late 2021. The name given by CrowdStrike to this framework is called IceApple. They have identified 18 modules that are integrated with IceApple and it is observed that it is still in development.
Understanding Assemblies
When you build a .NET assemblies the source code is compiled and stored as DLL (Dynamic Link Library) (generating libraries) or EXE file (Standalone). Standalone assemblies are simpler to develop and deploy. On the other hand DLLs are more complex but they offer more scalability.
.Net assemblies are stealthy hence are helpful for adversaries to evade the antivirus.
IceApple Versions
IceApple V1 was detected by OverWatch in 2021. This was detected because IIS doesn't load .Net assemblies from byte arrays in memory, Microsoft Exchange also doesn't load its .Net assemblies the way this framework did and lastly IIS file names are usually random, but the similarity was observed in the naming convention.
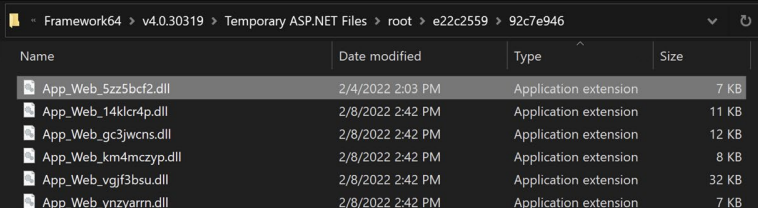
The source code was complete mess in IceApple V2. It was hybrid version of IceApple. It mimicked IIS compilation naming convention. This version included string obfuscation.
string.format("SA.M\SA.M.Do.main.....")
IceApple V3 had proper coding structure (better than V2). Devs ditched the random namespace and improved proper string obfuscation.
IceApple V4 had structural changes.
IceApple V5 added features for anti forensics. This version had "just in time encoding"
Read this detailed report by CrowdStrike here
TALK2: Talk on ShinyHunters
Speaker: Tyler & Austin
ShinyHunter is a decentralised group of blackhat hackers involved in stealing company's sensitive data and extortion. If ransom is not paid the threat actors leak/sell the data on darkweb. The members are active on multiple telegram groups with over thousands of messages and 12 admins.
Timeline (Major Incidents and companies)
The first breach was observed in Jan 2020. ShinyHunters stole 25million users data from company Mathway (app for solving algebric equetions). In May 2020 they stole over 500 GB of Microsoft source code from private repository. In 2021 they stole 70 million AT&T subscribers data including PII such as phone numbers and Social Security Number. In January 2021 they leaked 1.9 million user records from Pixlr. The list goes on including Legal Aid Agency (U.K. ministry of justice) and major companies like Salesforce, LVMH (Louis Vuitton), Google, Quantas and Jaguar Land Rover. (to read the list of hacks and more check this wikipedia page). Google Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG) later reported it as UNC6040, UNC6240 & UNC6395.
UNC6040
The attack path for UNC6040 starts with vishing and requesting user credentials. Upon access they extract data using Salesforce's Data Loader application. UNC6040 also uses salesforce apps hosted on Okta phishing panel to trick victims to visit from their work computer. To read more check this page.
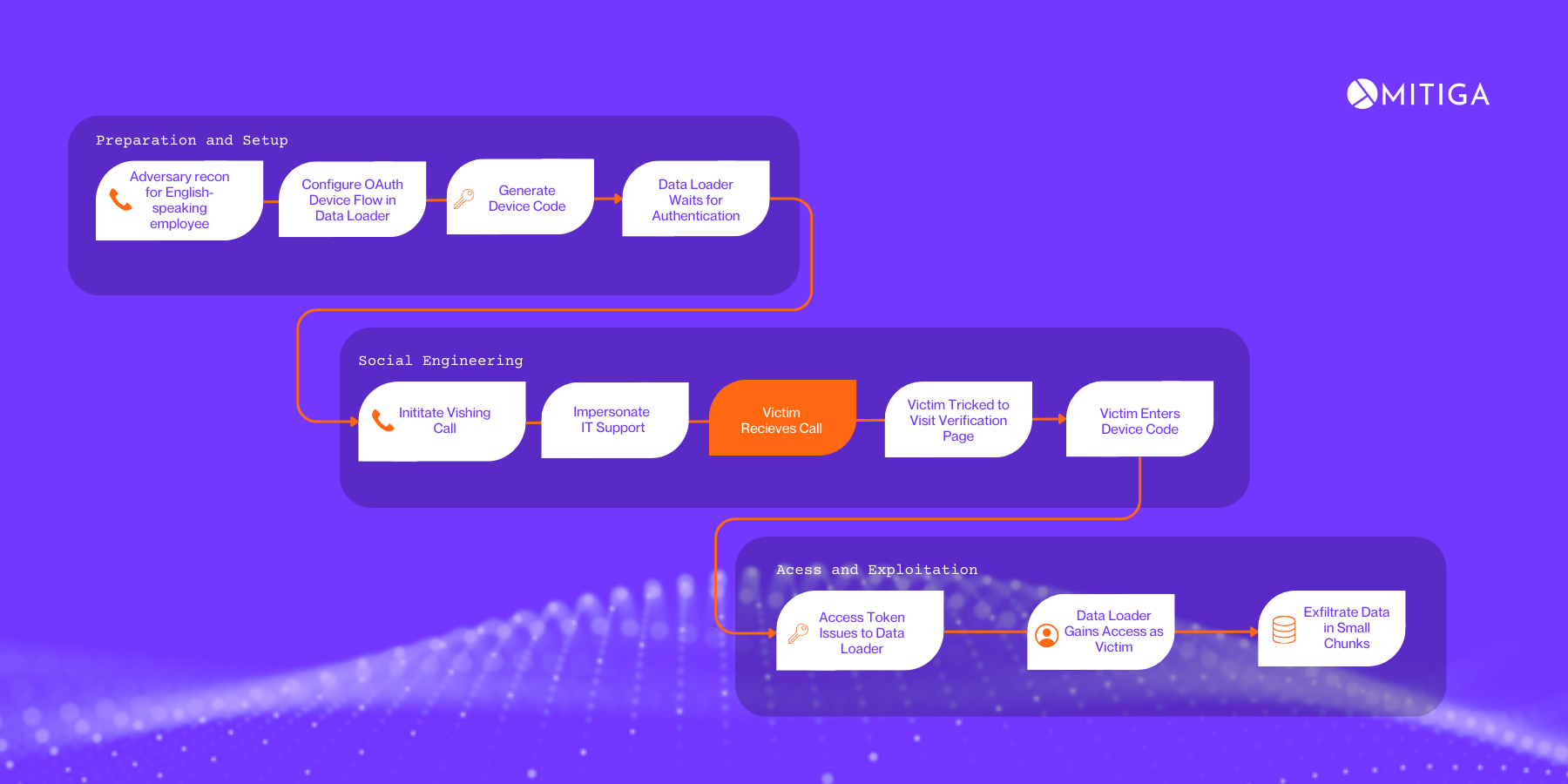
UNC6240
This was tracked by GTIG several months after UNC6040. This involve calls or emails to victim for ransom in bitcoin. UNC6240 consistently claimed to be ShinyHunters. It was reported that 40m+ customer data was leaked. 20 million dollars was the extortion amount however attackers received 1 million dollars. The email address of extortion groups are shinycorp@tuta.com and shinygroup@tuta.com
UNC6395
On Aug 2025, the UNC6395 leveraged compromised Salesloft Drift integration to gain access using SaaS supply-chain attack. Attacker exploited OAuth tokens from Salesloft Drift integration. These tokens are used to run queries and extract sensitive information from Salesforce and other connected apps. This lateral movement was possible due to weak policies in OAuth connection.
On 20th Aug 2025 Salesforce revoked the token terminating the attack. Check this report by FBI

Claims of ShinyHunters
Shiny hunters claims for UNC5537, UNC3944, SAP 0day, UNC6110 (stolen AWS keys) and UNC6209. They also claim for ties between SatterSpider threat group.
ShinyHunters claims for Jaguar cyberattack by providing the screenshot of the attack. Due to non payment of ransom they advertised 1 Billion records for 989.45 Million dollars.
They claim to have data of 1000 NSA and other government individuals.
This group claims the belonging of 5.7 million customer data from Quantas however FBI seizes and destroys the website linked to hackers threatening to release Quantas customer's data.
Next attack vectors
It is deduced that the next vectors of this attack group involve finding poorly secured keys/tokens to access restricted service and extract the data or exploit the service.
TALK3: Tracking a Cyber Espionage Campaign in South East Asia
Speaker: Andrew Ahmat & Jonathan Milford (Senior Threat Intel Analyst at Microsoft (both))
The talk starts with introduction of Radium APT-30 - a well known Chinese-state linked espionage group. This group is aka APT-C-30, Lotus Blossom, Raspberry Typhoon, Spring Dragon in some intelligence-vendor naming. It's main focus is governments, political bodies, media, defense, and other strategic sectors of Southeast Asia / ASEAN-region.
The talks further explains different types of clusters with their Certificate Authority. These clusters are used to extract PII such as phone emails. This was focused on Philippine government, economic and marine interests.
The talk shifts to MASOL RAT - a spying tool used by the threat group known as Earth Estries (also called Salt Typhoon). It acts like a remote controller that lets the attackers manage infected machines from far away. Researchers found clues in the file paths and code showing it has existed since around 2019, and newer versions mainly target Linux servers used by governments and telecom companies in Southeast Asia. The group usually breaks in by exploiting known vulnerabilities in public-facing systems like VPN appliances, then moves through the network using built-in admin tools to stay unnoticed. Once they gain a stable foothold, MASOL RAT is deployed to keep long-term access, run commands, steal data, and quietly communicate with the attackers’ servers. It fits into a bigger toolkit the group uses, showing how organized and patient this operation is. This makes MASOL RAT important for defenders to understand, especially for anyone protecting Linux-based infrastructure.
TALK4: Mining for Mithril in Open Directories
Speakers: Jason Smart
Mining threat actors becomes easy when threat actors has bad oppsec and week infrastructure - this lets us look at the huge amount of data they’ve collected, which often tells the real story.
Jason reveals that on 2023 around 38 GB data was collected from 32 IPs and in 2024 around 2.2 TB data was collected including 3315 directories.
The first and most important task is to identify what to mine. After that there are 2 types to collect the data - passive and active. Passive data collection strategy includes data collected from censys and virustotal. Jason shares various statistics including 406 mimikatz detections, 10k cslog files, 1126 webshells.
